Selected publications
For a full list please visit Google Scholar
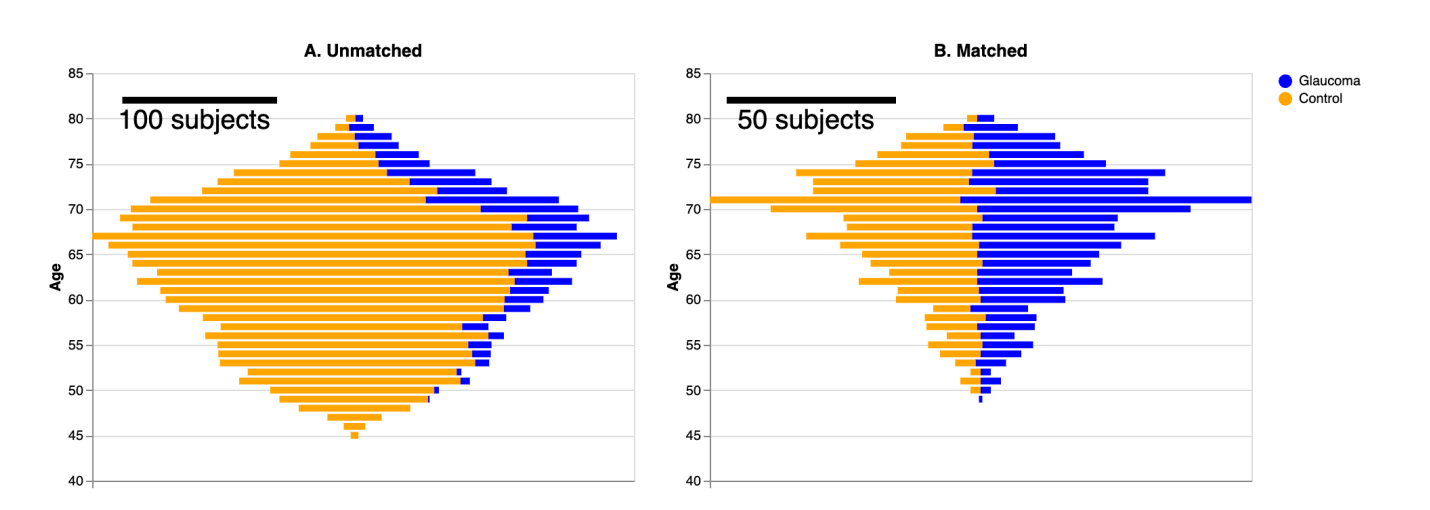
Sensory changes due to aging or disease can impact brain tissue. This study aims to investigate the link between glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness, and alterations in brain connections. We analyzed diffusion MRI measurements of white matter tissue in a large group, consisting of 905 glaucoma patients (aged 49-80) and 5292 healthy individuals (aged 45-80) from the UK Biobank. Confounds due to group differences were mitigated by matching a sub-sample of controls to glaucoma subjects. We compared classification of glaucoma using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) focusing on the optic radiations, which are the primary visual connection to the cortex, against those analyzing non-visual brain connections. As a control, we evaluated the performance of regularized linear regression models. We showed that CNNs using information from the optic radiations exhibited higher accuracy in classifying subjects with glaucoma when contrasted with CNNs relying on information from non-visual brain connections. Regularized linear regression models were also tested, and showed significantly weaker classification performance. Additionally, the CNN was unable to generalize to the classification of age-group or of age-related macular degeneration. Our findings indicate a distinct and potentially non-linear signature of glaucoma in the tissue properties of optic radiations. This study enhances our understanding of how glaucoma affects brain tissue and opens avenues for further research into how diseases that affect sensory input may also affect brain aging.
John Kruper, Adam Richie-Halford, Noah C Benson, Sendy Caffarra, Julia Owen, Yue Wu, Catherine Egan, Aaron Y Lee, Cecilia S Lee, Jason D Yeatman, Ariel Rokem & UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium
Communications Medicine volume 4, Article number: 72 (2024)
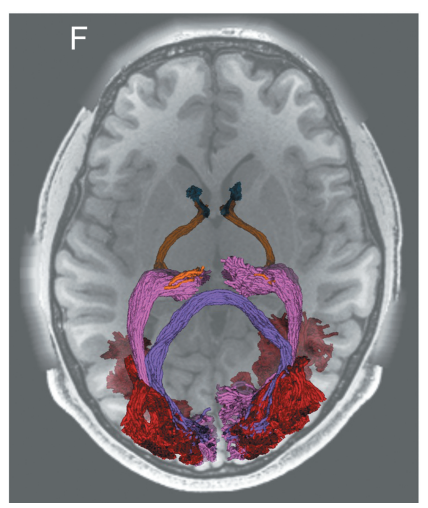
Diffusion-weighted MRI (dMRI) provides a unique non-invasive view of human brain tissue properties. The present review article focuses on tractometry analysis methods that use dMRI to assess the properties of brain tissue within the long-range connections comprising brain networks. We focus specifically on the major white matter tracts that convey visual information. These connections are particularly important because vision provides rich information from the environment that supports a large range of daily life activities. Many of the diseases of the visual system are associated with advanced aging, and tractometry of the visual system is particularly important in the modern aging society. We provide an overview of the tractometry analysis pipeline, which includes a primer on dMRI data acquisition, voxelwise model fitting, tractography, recognition of white matter tracts, and calculation of tract tissue property profiles. We then review dMRI-based methods for analyzing visual white matter tracts: the optic nerve, optic tract, optic radiation, forceps major, and vertical occipital fasciculus. For each tract, we review background anatomical knowledge together with recent findings in tractometry studies on these tracts and their properties in relation to visual function and disease. Overall, we find that measurements of the brain’s visual white matter are sensitive to a range of disorders and correlate with perceptual abilities. We highlight new and promising analysis methods, as well as some of the current barriers to progress toward integration of these methods into clinical practice. These barriers, such as variability in measurements between protocols and instruments, are targets for future development.
Hiromasa Takemura, John Kruper, Toshikazu Miyata, & Ariel Rokem
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, 23(3), 2024
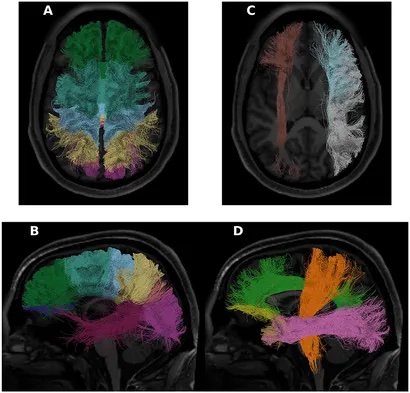
The Human Connectome Project (HCP) has become a keystone dataset in human neuroscience, with a plethora of important applications in advancing brain imaging methods and an understanding of the human brain. We focused on tractometry of HCP diffusion-weighted MRI (dMRI) data. We used an open-source software library (pyAFQ; https://yeatmanlab.github.io/pyAFQ) to perform probabilistic tractography and delineate the major white matter pathways in the HCP subjects that have a complete dMRI acquisition (n = 1,041). We used diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) to model white matter microstructure in each voxel of the white matter, and extracted tract profiles of DKI-derived tissue properties along the length of the tracts. We explored the empirical properties of the data: first, we assessed the heritability of DKI tissue properties using the known genetic linkage of the large number of twin pairs sampled in HCP. Second, we tested the ability of tractometry to serve as the basis for predictive models of individual characteristics (e.g., age, crystallized/fluid intelligence, reading ability, etc.), compared to local connectome features. To facilitate the exploration of the dataset we created a new web-based visualization tool and use this tool to visualize the data in the HCP tractometry dataset. Finally, we used the HCP dataset as a test-bed for a new technological innovation: the TRX file-format for representation of dMRI-based streamlines. We released the processing outputs and tract profiles as a publicly available data resource through the AWS Open Data program’s Open Neurodata repository. We found heritability as high as 0.9 for DKI-based metrics in some brain pathways. We also found that tractometry extracts as much useful information about individual differences as the local connectome method. We released a new web-based visualization tool for tractometry—“Tractoscope” (https://nrdg.github.io/tractoscope). We found that the TRX files require considerably less disk space-a crucial attribute for large datasets like HCP. In addition, TRX incorporates a specification for grouping streamlines, further simplifying tractometry analysis.
John Kruper, McKenzie P Hagen, François Rheault, Isaac Crane, Asa Gilmore, Manjari Narayan, Keshav Motwani, Eardi Lila, Chris Rorden, Jason D Yeatman & Ariel Rokem
Front. Neurosci., 11 June 2024
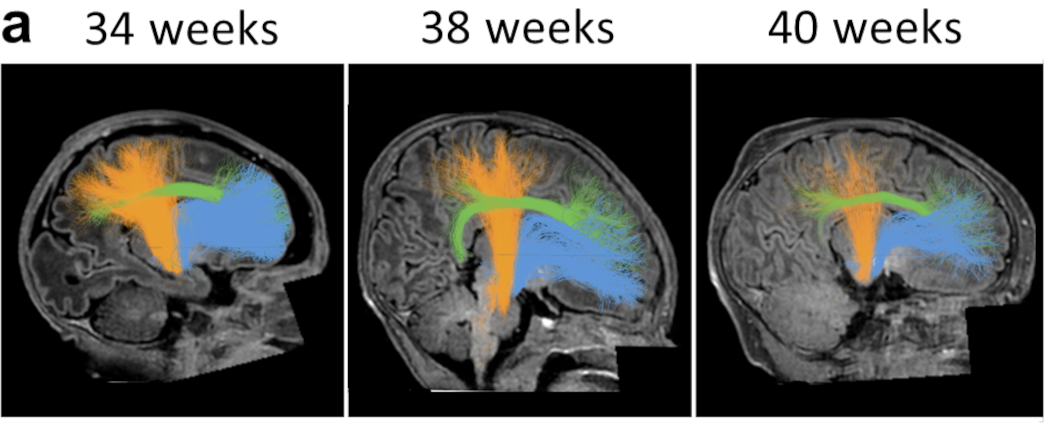
The formation of myelin, the fatty sheath that insulates nerve fibers, is critical for healthy brain function. A fundamental open question is what impact being born has on myelin growth. To address this, we evaluated a large (n=300) cross-sectional sample of newborns from the Developing Human Connectome Project (dHCP). First, we developed new software for the automated identification of 20 white matter bundles in individuals that is well-suited for large samples. Next, we fit linear models that quantify how T1w/T2w (a myelin-sensitive imaging contrast) changes over time at each point along the bundles. We found faster growth of T1w/T2w along the lengths of all bundles before birth than right after birth. Further, in a separate longitudinal sample of preterm infants (N=34), we found lower T1w/T2w than in full-term peers measured at the same age. By applying the linear models fit on the cross-section sample to the longitudinal sample of preterm infants, we find that their delay in T1w/T2w growth is well explained by the amount of time they spent developing in utero and ex utero. These results suggest that white matter myelinates faster in utero than ex utero . The reduced rate of myelin growth after birth, in turn, explains lower myelin content in individuals born preterm, and could account for long-term cognitive, neurological, and developmental consequences of preterm birth. We hypothesize that closely matching the environment of infants born preterm to what they would have experienced in the womb may reduce delays in myelin growth and hence improve developmental outcomes.
Mareike Grotheer, David Bloom, John Kruper, Adam Richie-Halford, Stephanie Zika, Vicente A. Aguilera González, Jason D. Yeatman, Kalanit Grill-Spector & Ariel Rokem
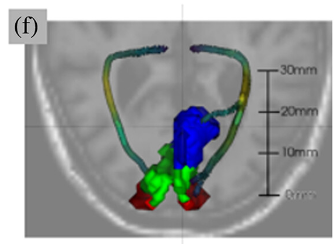
The neural pathways that carry information from the foveal, macular, and peripheral visual fields have distinct biological properties. The optic radiations (OR) carry foveal and peripheral information from the thalamus to the primary visual cortex (V1) through adjacent but separate pathways in the white matter. Here, we perform white matter tractometry using pyAFQ on a large sample of diffusion MRI (dMRI) data from subjects with healthy vision in the U.K. Biobank dataset (UKBB; N = 5,382; age 45–81). We use pyAFQ to characterize white matter tissue properties in parts of the OR that transmit information about the foveal, macular, and peripheral visual fields, and to characterize the changes in these tissue properties with age. We find that (1) independent of age there is higher fractional anisotropy, lower mean diffusivity, and higher mean kurtosis in the foveal and macular OR than in peripheral OR, consistent with denser, more organized nerve fiber populations in foveal/parafoveal pathways, and (2) age is associated with increased diffusivity and decreased anisotropy and kurtosis, consistent with decreased density and tissue organization with aging. However, anisotropy in foveal OR decreases faster with age than in peripheral OR, while diffusivity increases faster in peripheral OR, suggesting foveal/peri-foveal OR and peripheral OR differ in how they age.
John Kruper, Noah C. Benson, Sendy Caffarra, Julia Owen, Yue Wu, Aaron Y. Lee, Cecilia S. Lee, Jason D. Yeatman, Ariel Rokem & UK Biobank Eye and Vision Consortium
Human Brain Mapping 44 (8), 3123-3135
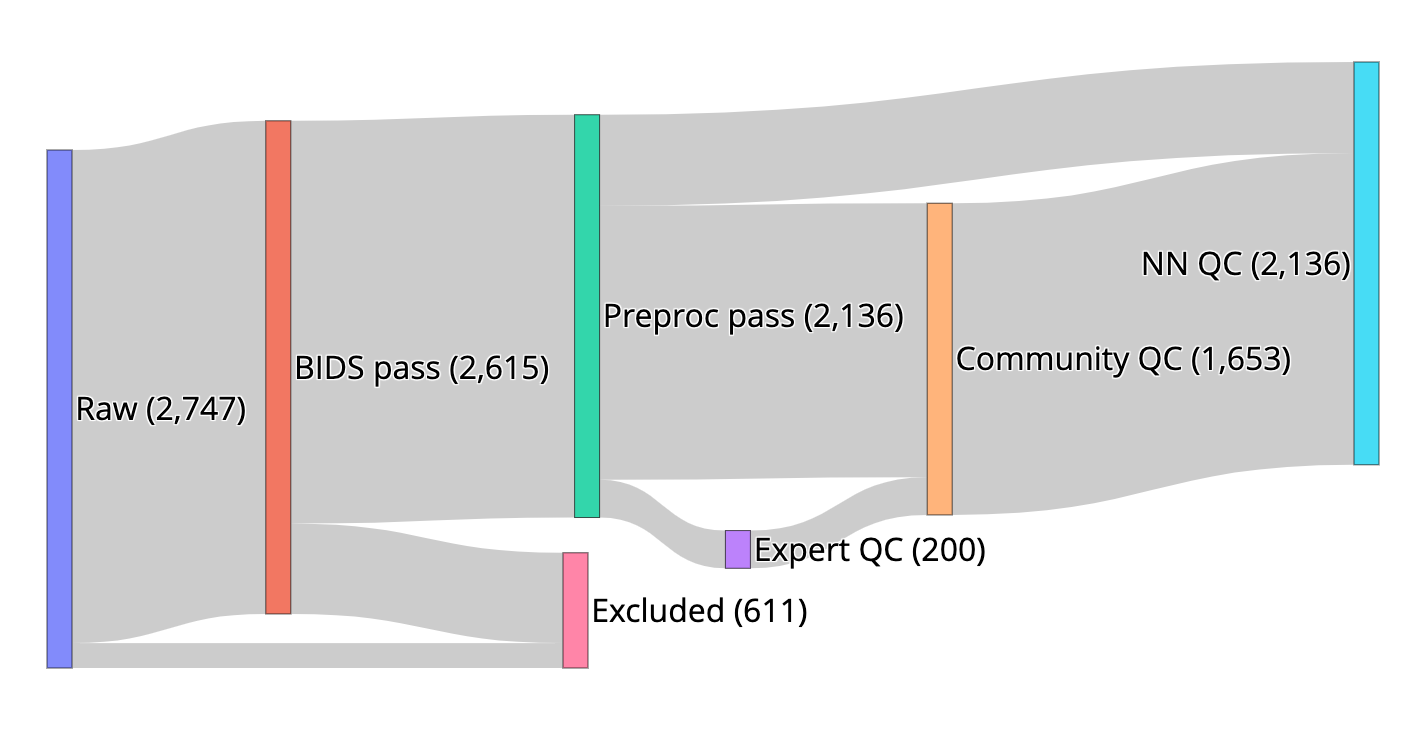
We created resources to facilitate research on the role of human brain microstructure in the development of mental health disorders, based on openly-available diffusion MRI (dMRI) data from the Healthy Brain Network (HBN) study. First, we curated the HBN dMRI data (N=2,747) into the Brain Imaging Data Structure and preprocessed it according to best-practices, including denoising and correcting for motion effects, susceptibility-related distortions, and eddy currents. Preprocessed, analysis-ready data was made openly available. Data quality plays a key role in the analysis of dMRI, and we provide automated quality control (QC) scores for every scan, as part of the data release. To scale QC to this large dataset, we trained a neural network through the combination of a small data subset scored by experts and a larger set scored by community scientists. The network performs QC highly concordant with that of experts on a held out set (ROC-AUC = 0.947). A further analysis of the neural network demonstrates that it relies on image features with relevance to QC. Altogether, this work both delivers a resource for transdiagnostic research in brain connectivity and pediatric mental health and serves as a novel tool for automated QC of large datasets.
Adam Richie-Halford, Matthew Cieslak, Lei Ai, Sendy Caffarra, Sydney Covitz, Alexandre R. Franco, Iliana I. Karipidis, John Kruper, Michael Milham, Bárbara Avelar-Pereira, Ethan Roy, Valerie J. Sydnor, Jason Yeatman, The Fibr Community Science Consortium, Theodore D. Satterthwaite, Ariel Rokem
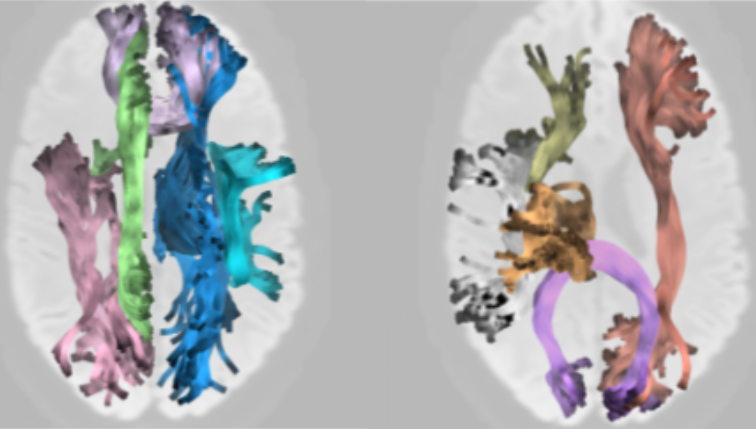
The validity of research results depends on the reliability of analysis methods. In recent years, there have been concerns about the validity of research that uses diffusion-weighted MRI (dMRI) to understand human brain white matter connections in vivo, in part based on reliability of the analysis methods used in this field. We defined and assessed three dimensions of reliability in dMRI-based tractometry, an analysis technique that assesses the physical properties of white matter pathways: (1) reproducibility, (2) test-retest reliability and (3) robustness. To facilitate reproducibility, we provide software that automates tractometry (https://yeatmanlab.github.io/pyAFQ). In measurements from the Human Connectome Project, as well as clinical-grade measurements, we find that tractometry has high test-retest reliability that is comparable to most standardized clinical assessment tools. We find that tractometry is also robust: showing high reliability with different choices of analysis algorithms. Taken together, our results suggest that tractometry is a reliable approach to analysis of white matter connections. The overall approach taken here both demonstrates the specific trustworthiness of tractometry analysis and outlines what researchers can do to demonstrate the reliability of computational analysis pipelines in neuroimaging.
John Kruper, Jason Yeatman, Adam Richie-Halford, David Bloom, Mareike Grotheer, Sendy Caffarra, Gregory Kiar, Iliana Karipidis, Ethan Roy & Ariel Rokem
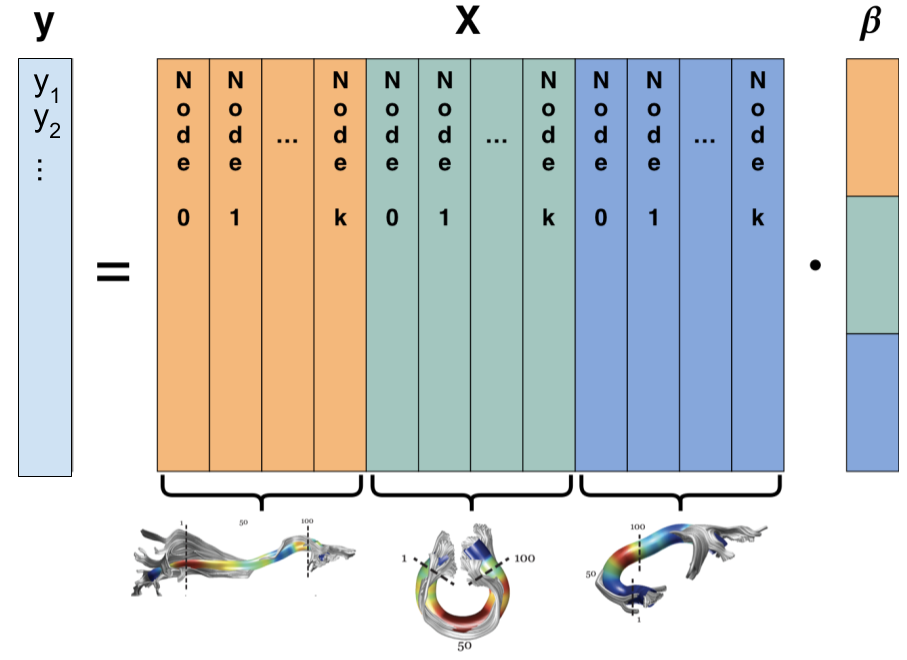
The white matter contains long-range connections between different brain regions and the organization of these connections holds important implications for brain function in health and disease. Tractometry uses diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) data to quantify tissue properties along the trajectories of these connections. In the present work, we developed a method based on the sparse group lasso (SGL) that takes into account tissue properties measured along all of the bundles, and selects informative features by enforcing sparsity, not only at the level of individual bundles, but also across the entire set of bundles and all of the measured tissue properties. The sparsity penalties for each of these constraints is identified using a nested cross-validation scheme that guards against over-fitting and simultaneously identifies the correct level of sparsity. SGL makes it possible to leverage the multivariate relationship between diffusion properties measured along multiple bundles to make accurate predictions of subject characteristics while simultaneously discovering the most relevant features of the white matter for the characteristic of interest.
Adam Richie-Halford, Jason Yeatman, Noah Simon & Ariel Rokem
PLoS Computational Biology: 17(6): e1009136
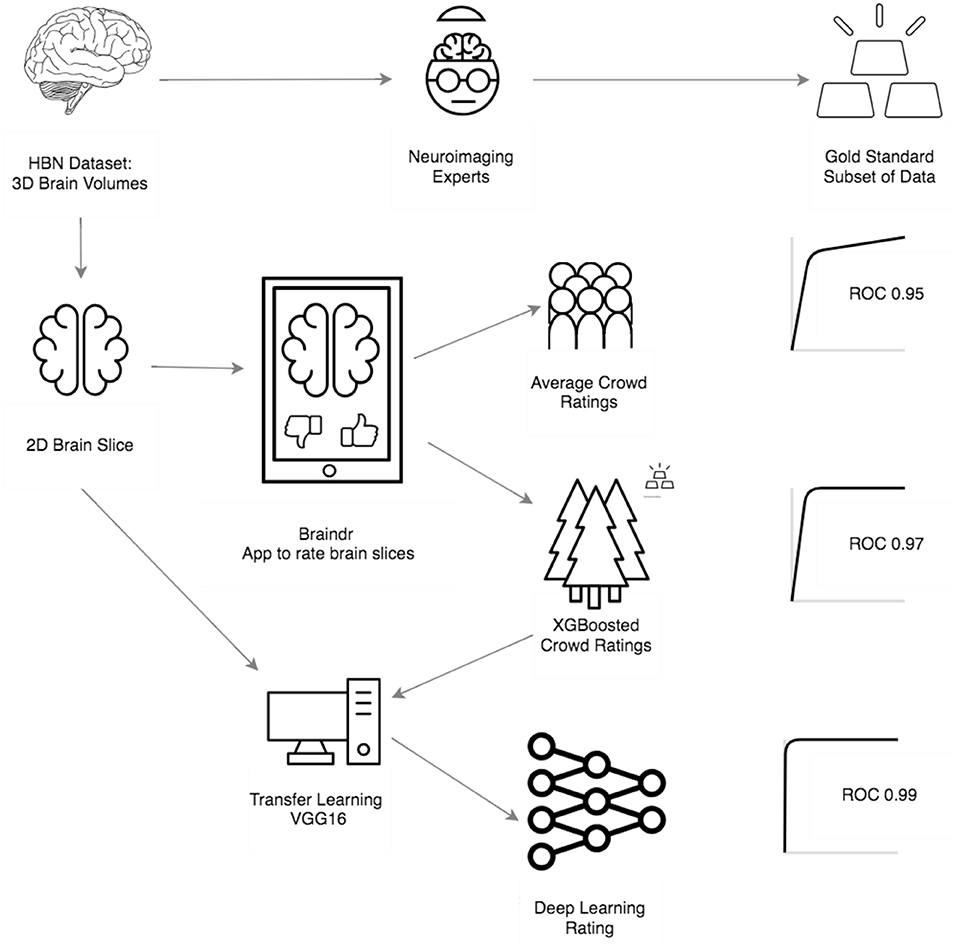
Combining citizen science and deep learning can generalize and scale expert decision making; this is particularly important in disciplines where specialized, automated tools do not yet exist. In Braindr, expert-labeled data were amplified by citizen scientists through a simple web interface. A deep learning algorithm was then trained to predict data quality, based on citizen scientist labels. Deep learning performed as well as specialized algorithms for quality control (AUC = 0.99).
Anisha Keshavan, Jason Yeatman & Ariel Rokem
Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 13: 29
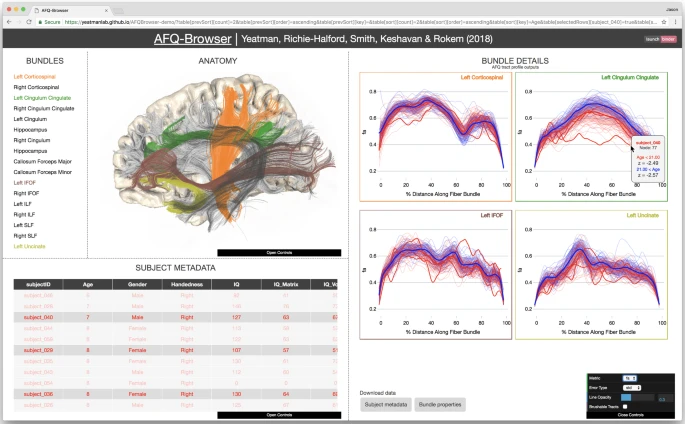
Human neuroscience research faces several challenges with regards to reproducibility. While scientists are generally aware that data sharing is important, it is not always clear how to share data in a manner that allows other labs to understand and reproduce published findings. Here we report a new open source tool, AFQ-Browser, that builds an interactive website as a companion to a diffusion MRI study. Because AFQ-Browser is portable—it runs in any web-browser—it can facilitate transparency and data sharing. Moreover, by leveraging new web-visualization technologies to create linked views between different dimensions of the dataset (anatomy, diffusion metrics, subject metadata), AFQ-Browser facilitates exploratory data analysis, fueling new discoveries based on previously published datasets. In an era where Big Data is playing an increasingly prominent role in scientific discovery, so will browser-based tools for exploring high-dimensional datasets, communicating scientific discoveries, aggregating data across labs, and publishing data alongside manuscripts.
Jason Yeatman, Adam Richie-Halford, Josh Smith, Anisha Keshavan & Ariel Rokem
Nature Communications: 9, Article number: 940